Many farmers wonder why their plants are growing slowly, why leaves are turning yellow, or why plants are wilting. Often, these issues can be traced back to fluctuations in soil pH, making it crucial to check and amend the soil.
In this article, we will explore what soil pH is, how it affects plant growth, and methods for testing soil pH to ensure timely interventions for your field.
- Definition: Soil pH measures the acidity or alkalinity of soil, ranging from 1 to 14. It reflects whether the soil is acidic, neutral, or alkaline. Most soils have a pH between 5.0 and 8.0. Each plant species has an optimal pH range; if the pH deviates from this range, plants may experience stunted growth, yellowing leaves, wilting, or even death.
- Soil Classification by pH:
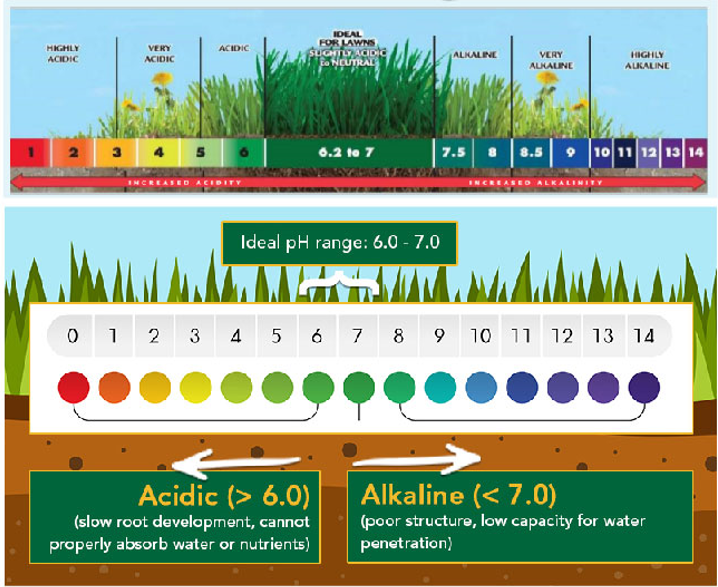 Soil pH scale and how it affects plants
Soil pH scale and how it affects plants
Note: Measure soil pH at any time, but avoid testing immediately after applying lime, fertilizers, or organic matter, as this can skew results.

3 stages need to check soil pH
Soil pH can serve as an indicator of various soil problems. Timely identification allows for appropriate interventions to prevent crop damage.
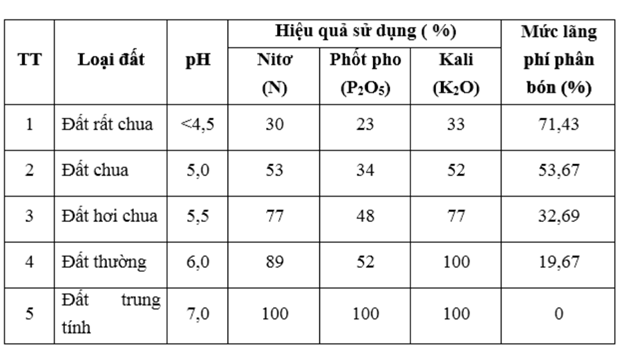
Table evaluating the influence of pH on fertilizer use efficiency.
Effects of pH on Nutrient Availability:
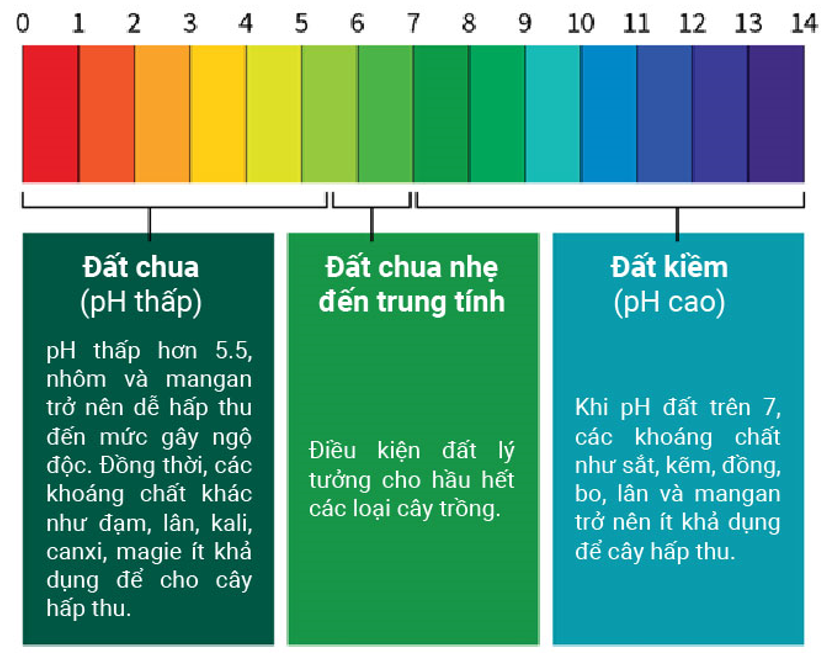
The impact of soil pH on the soil environment.
- Create a hole in the soil using a drill or ruler (ensure consistent depth for each measurement).
- Add distilled or deionized water to moisten the soil, avoiding excess water.
- Insert the pH meter probe into the hole and wait for the reading.
- Collect representative samples from various locations in the planting area, including near plants and at least two samples further away.
- Mark the pH at sampling points, as nutrient levels and soil type can fluctuate.
- Mix about 0.5 kg of soil, let it dry, then crush and weigh 0.1 kg for testing.
- Place the sample in a 0.5-liter beaker, add 2/3 water, and stir until dissolved.
- After 30 minutes, pour off the upper layer of water for testing.
- Dip a pH test strip into the solution until the paper is fully saturated. Wait one minute for color change.
- Compare the strip color with a pH color chart to determine soil pH.
- Mix soil with distilled water in a measuring container, adding a few reagents.
- Follow instructions to see color changes indicating pH levels.
- Digital pH Meters: These provide accurate readings displayed on an LCD screen, are less affected by solution color, and have a lower error margin (0.01-0.1).
- pH Testing Kits: Offer high precision but require careful handling and are more expensive.
- Laboratory Chemicals: For precise testing, requiring a lab setting and knowledgeable personnel.

Top 5 most accurate ways to measure soil pH.
Soil pH significantly impacts both soil health and plant growth. By understanding soil pH, you can manage and enhance the growth of your crops effectively.
This guide aims to help you recognize the signs of plant distress such as wilting, yellowing leaves, or slow growth, enabling you to check soil pH and assess its effects. With this knowledge, you can implement the appropriate measures to restore your field’s health.
For further advice on handling acidic or alkaline soil conditions, consult ATW’s additional resources or contact our support engineers 24/7 at hotline 032 988 6079.